Use this calculator to estimate how much CO2 your electricity consumption generates. If you know how much kWh of electricity you are consuming, and you look up the percentage of the electricity being produced by fossil fuels using the links we have provided, you can calculate how many pounds or kilograms of CO2 you are producing.
Read below to learn how the calculator works to calculate those carbon emissions. Additionally, an explanation is provided for the reason why we include EU carbon permits expense and why it should matter to Americans and other citizens of the world. Finally, we announce which states in America have the highest and lowest carbon emissions from grid power and overall.
How to calculate the amount of CO2 your local grid produces from the electricity you consume
Calculate the CO2 your electricity consumption generates. To calculate the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) generated from grid fossil-fuel-burning power plants, you will need to know the following:
- The amount of electricity consumed (in kilowatt-hours or kWh) by the device or appliances you are interested in.
- The carbon intensity of the electricity generated by the power plant, which is measured in kilograms of CO2 emissions per kWh.
- The percentage of the grid’s electricity from either natural gas, coal, or petroleum.
Here are the steps to calculate CO2 generated from grid fossil-fuel-burning power plants:
- Determine the amount of electricity consumed by the device or appliances in question. This can usually be found on the device’s label or in the user manual. For example, let’s say a computer uses 0.3 kWh of electricity in a day. The way is to look at your electricity bill to see what your total kWh consumption was for the billing period.
- Find out the carbon intensity of the electricity generated by the power plant. This information can usually be obtained from the utility company that supplies your electricity or from government sources. For example, let’s say the carbon intensity of the electricity generated by the power plant is 0.5 kg CO2 emissions per kWh.
- Multiply the electricity consumed by the carbon intensity to get the amount of CO2 generated. Using the example above, we would multiply 0.3 kWh by 0.5 kg CO2 per kWh to get 0.15 kg CO2 generated in a day.
If you want to calculate the amount of CO2 generated over a longer period, such as a month or a year, simply multiply the daily amount by the number of days in the period.
It’s worth noting that the carbon intensity of electricity can vary depending on the type of fossil fuel used, the efficiency of the power plant, and other factors. Therefore, the carbon intensity used in the calculation may not be precise, but it should give you a rough estimate of the amount of CO2 generated from grid fossil-fuel-burning power plants.
What are EU Carbon Permits and why do they matter?
EU Carbon Permits are a type of permit that allows companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. They are part of the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (ETS), which is designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industries and power generation in Europe.
The European Union’s Emissions Trading System (ETS) forces manufacturers, power companies, and airlines to pay for each ton of carbon dioxide they emit as part of Europe’s efforts to meet its climate targets. EU Allowances are expected to average 81.40 euros a ton in 2023 and 94.14 euros in 2024, up 4.2% and 1.9%, respectively, from forecasts made in October, according to Reuters.
Under the ETS, companies in certain sectors, such as power generation, cement production, and steel manufacturing, are required to hold permits to emit a certain amount of CO2. These permits are known as EU Carbon Permits, and they can be bought and sold on the carbon market. Companies that emit less CO2 than their allotted permit can sell their excess permits to companies that emit more CO2 than their permits allow.
The goal of the ETS and the EU Carbon Permits is to create a financial incentive for companies to reduce their carbon emissions. By making it more expensive to emit CO2, companies are encouraged to invest in cleaner technologies and reduce their overall carbon footprint. In addition, the system creates a mechanism for countries and companies to work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in a coordinated and efficient manner.
The EU Carbon Permits matter because they are a key tool in Europe’s efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. By creating a market for carbon permits, the ETS creates a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions, which can help to drive innovation and investment in clean technologies. Additionally, the ETS is seen as a model for other countries and regions looking to implement similar systems to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Understanding the cost of carbon emissions is important because it is just a matter of time before all of the USA will be covered by a similar system.
Does the US have anything like EU Carbon Permits already?
Yes, the US has a similar program to the EU Carbon Permits called the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI). The RGGI is a cap-and-trade program that covers power plants in 11 states in the northeastern US, including Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia.
Under the RGGI program, power plants must hold permits for their carbon emissions, which are auctioned off by the participating states. The states collectively set a cap on the amount of carbon emissions allowed by the power plants, and the cap is reduced over time to encourage emissions reductions. Companies that emit less than their allotted emissions can sell their excess permits to companies that exceed their emissions limit.
The RGGI program is designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector, which is one of the largest sources of emissions in the US. The program aims to reduce emissions from power plants by 30% by 2030, compared to 2005 levels. The program has been in place since 2009 and has been credited with reducing emissions and driving investment in clean energy technologies in the participating states.
It’s worth noting that while the RGGI is a regional program and does not cover the entire US, it serves as an example of how cap-and-trade programs can be implemented to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in a coordinated and market-based manner.
Does the SEC require greenhouse gas emissions reporting?

Bloomberg Law has reported that the SEC has proposed new climate-related disclosure requirements for public companies. In March 2022, with the “issuer rule,” the SEC proposed rule amendments that would require public companies to provide certain climate-related financial data, and greenhouse gas emissions insights, in public disclosure filings. As part of the issuer rule, companies would have to disclose emissions they are directly responsible for, as well as emissions from their supply chains and products.
US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) currently does not require mandatory greenhouse gas emissions reporting for publicly traded companies. However, the SEC has been exploring the possibility of requiring climate-related disclosures in its corporate reporting requirements. After issuer rule comment periods, the SEC will consider whether to issue further amendments and adopt the proposal. Legal experts predict the SEC will finalize and adopt the issue rule – in some version – in 2023.
In February 2021, the SEC announced that it would begin reviewing its disclosure rules with a focus on climate-related risks and opportunities. The agency sought public input on how companies should report climate-related risks and opportunities in their financial statements, including their greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, the SEC issued guidance in 2010 that requires companies to disclose material climate-related risks in their financial statements if such risks could have a material impact on the company’s financial performance. This guidance was issued as part of the SEC’s interpretation of existing disclosure requirements, rather than as a new rule.
It’s worth noting that some companies voluntarily report their greenhouse gas emissions, either as part of their sustainability reporting or in response to stakeholder demands. Additionally, some investors and other stakeholders are pushing for mandatory climate-related disclosures from the SEC and other regulatory agencies.
Which state in America has the lowest carbon emissions from its electrical grid?
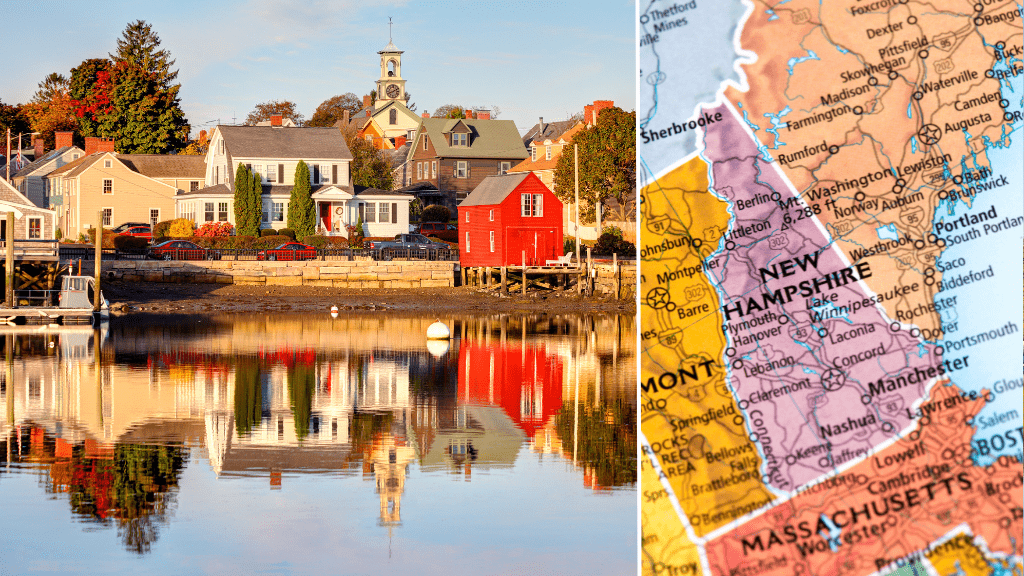
As of September 2021, the state in America with the lowest carbon emissions from its electrical grid was New Hampshire. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2019, the state’s electrical grid emitted the least amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) per unit of electricity generated compared to all other states in the country.
New Hampshire’s low carbon emissions are due to a variety of factors, including the state’s high use of non-fossil fuel sources of electricity generation such as nuclear and hydroelectric power. In 2019, these two sources accounted for nearly three-quarters of the state’s electricity generation. Additionally, New Hampshire has implemented energy efficiency measures and renewable portfolio standards which have helped to reduce carbon emissions from its electrical grid.
It’s important to note that these rankings can change over time, as states may take different approaches to their energy policies and renewable energy development.
Which state in a America has the lowest carbon emissions?
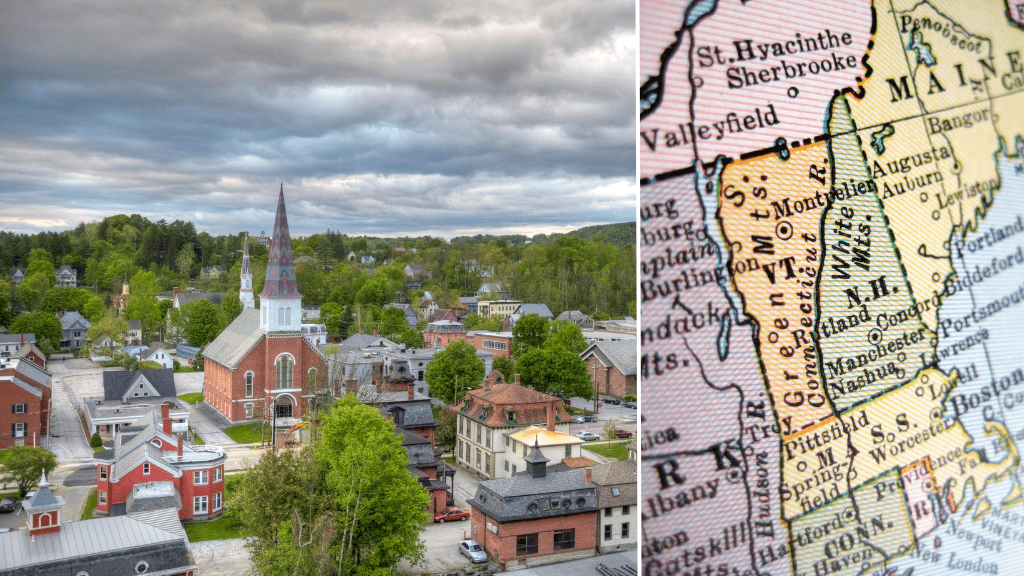
As of September 2021, the state in America with the lowest carbon emissions was Vermont. Vermont has a relatively low population and relies heavily on renewable energy sources, particularly hydropower and biomass. In addition, the state has implemented aggressive policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including setting a goal of achieving 90% renewable energy by 2050 and implementing a carbon tax.
As a result, Vermont has been able to significantly reduce its carbon emissions and is consistently ranked among the states with the lowest per capita carbon emissions in the United States. However, it’s important to note that carbon emissions can fluctuate over time, and other states may have taken significant steps towards reducing their emissions in recent years.
Which state in America has the highest carbon emissions from its electrical grid?
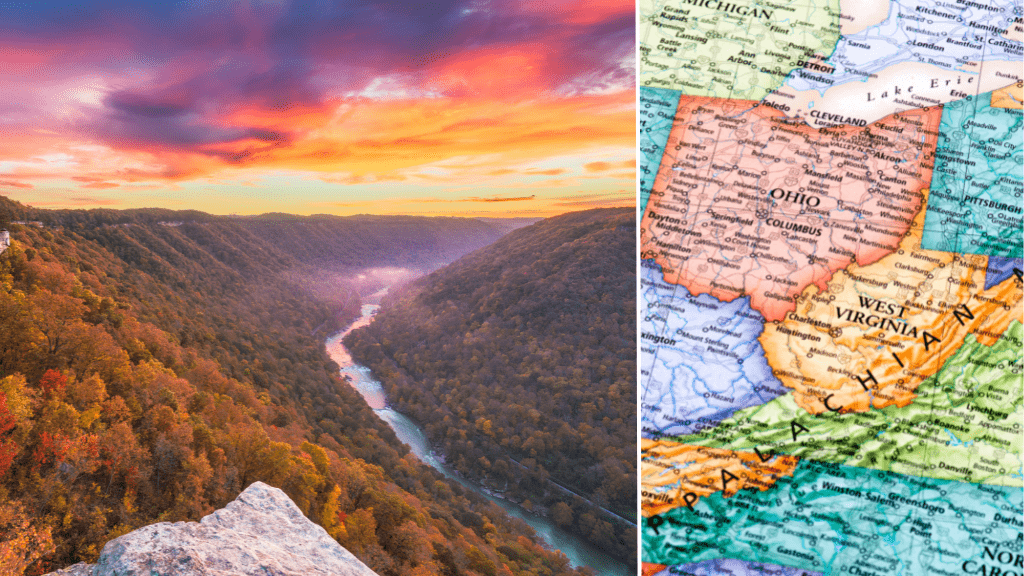
As of September 2021, the state in America with the highest carbon emissions from its electrical grid was West Virginia. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2019, West Virginia had the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per unit of electricity generated compared to all other states in the country.
West Virginia’s high carbon emissions are due to its heavy reliance on coal-fired power plants for electricity generation. Coal accounts for more than 90% of the state’s electricity generation, and as a result, its electrical grid produces a relatively high amount of CO2 emissions per unit of electricity generated.
If you live or work in West Virginia, you may be interested to calculate the CO2 your electricity consumption generates. In 2021, coal-fired electric power plants accounted for 91% of West Virginia’s total electricity net generation. Renewable energy resources—primarily hydroelectric power and wind energy—contributed 5% and natural gas provided more than 4%. Using our calculator above, when you change the percentage mix for natural gas to 4% and coal to 91%, the amount of carbon emissions produced in West Virginia for 100 kWh is estimated at 230 lbs. released into the atmosphere.
If a system similar to EU carbon permits were to be in place, that would cost businesses in West Virginia consuming that carbon-intensive energy an additional $11.12. The additional tax from a future national carbon trading system would create a significant disincentive for energy intensive businesses to locate in West Virginia. For existing businesses, the potential of the additional costs attached to CO2 emissions would represent a significant future liability. It is therefore in West Virginia’s economic interests to aggressively decarbonize its grid power prior to such a carbon trading scheme be put in place.
In 2023, if the SEC GHG disclosures rule is adopted, companies in West Virginia may need to report the 230 lbs. of CO2 per 100 kWh of electricity consumed. It is possible that being a laggard in decarbonizing may be punished by Wall Street investment firms. This is another reason for businesses to lobby West Virginia law-makers to accelerate the decarbonization of its power generation system. Another strategy would be for West Virginia businesses to invest in green hydrogen fuel cells for its fleets of powered industrial trucks and over the road heavy-duty transportation vehicles.
Remember, these rankings can change over time, as states may take different approaches to their energy policies and renewable energy development. The calculator we use is based on publicly available information, but is provided for discussion purposes only. It is not a scientific report and all estimates should be confirmed by climate experts. Additionally, it’s worth noting that several states have set ambitious targets for transitioning to renewable energy sources, which could help reduce carbon emissions from their electrical grids over time.
Which state in a America has the highest carbon emissions?
As of September 2021, the state in America with the highest carbon emissions was Texas. Texas is a large state with a high population and a significant industrial sector, which contributes to its high carbon emissions. In addition, Texas relies heavily on fossil fuels for electricity generation, particularly coal and natural gas.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2019, Texas was responsible for the highest level of energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions of any state in the United States, accounting for about 9% of the national total. The state’s transportation sector was also a major contributor to its overall carbon emissions.
If you live or work in Texas, you may also be interested to calculate the CO2 your electricity consumption generates. In 2019, coal-fired electric power plants accounted for 20.3% of Texas’s total electricity net generation. Renewable energy resources—primarily wind energy—contributed 20% and natural gas provided more than 47.4%. Nuclear, which is a zero carbon source of electricity, was 10.8% of Texas’ total electrical energy grid generation by fuel source. Using our calculator above, when you change the percentage mix for natural gas to 47.4% and coal to 20.3%, the amount of carbon emissions produced in Texas for 100 kWh is estimated at 70.28 lbs. released into the atmosphere.
Following the example used for West Virginia above, if a system similar to EU carbon permits were to be in place, the 70.28 lbs. of carbon dioxide would cost businesses in Texas consuming that carbon-intensive energy an additional $3.40 for every 100 kWh. The additional tax from a future national carbon trading system would create a significant disincentive for energy intensive businesses to locate in Texas. For existing businesses, the potential of the additional costs attached to CO2 emissions would represent a significant future liability. It is therefore in Texas’ economic interests to aggressively decarbonize its grid power prior to such a carbon trading scheme be put in place.
A final reminder that one should keep in mind that carbon emissions can vary over time, and states may take different approaches to reducing their emissions through renewable energy development and energy efficiency measures.
We have calculated the CO2 electricity consumption generated in other places in North America – lbs./100 kWh
If you live in Ontario, Canada, the province with the largest economic output of all the Canadian provinces, you produce 32.89 lbs. of carbon dioxide per 100 kWh consumed. Compare this other areas around North America:
Quebec is the second largest economy in Canada and you can expect to produce a measly 0.59 lbs. of CO2 when you consume 100 kWh of electricity.
Compare that to:
- 0.1 lbs./100 kWh in Vermont
- 45.76 lbs./100 kWh in California
- 87.26 lbs./100 kWh in Florida
- 70.28 lbs./100 kWh in Texas
- 230 lbs./100 kWh in West Virginia
Calculate the amount of CO2 you produce when you consume electricity
You can look up the carbon intensity of the electricity in your USA state at this link. Choose your state from the dropdown list called “Change State/Territory”. Look for the the blue block titled, “Supply & Distribution”. There you can click the light blue triangle to see the “Utility-Scale Net Electricity Generation (share of total) table for the sources of energy used to produce the electricity you consume.





